PHP 7 Data types: The values assigned to a PHP variable may be of different data types including simple string and numeric types to more complex data types like arrays and objects.
PHP supports a total of eight primitive data types: Integer, Floating point number or Float, String, Booleans, Array, Object, resource, and NULL. These data types are used to construct variables. Now let’s discuss each one of them in detail.
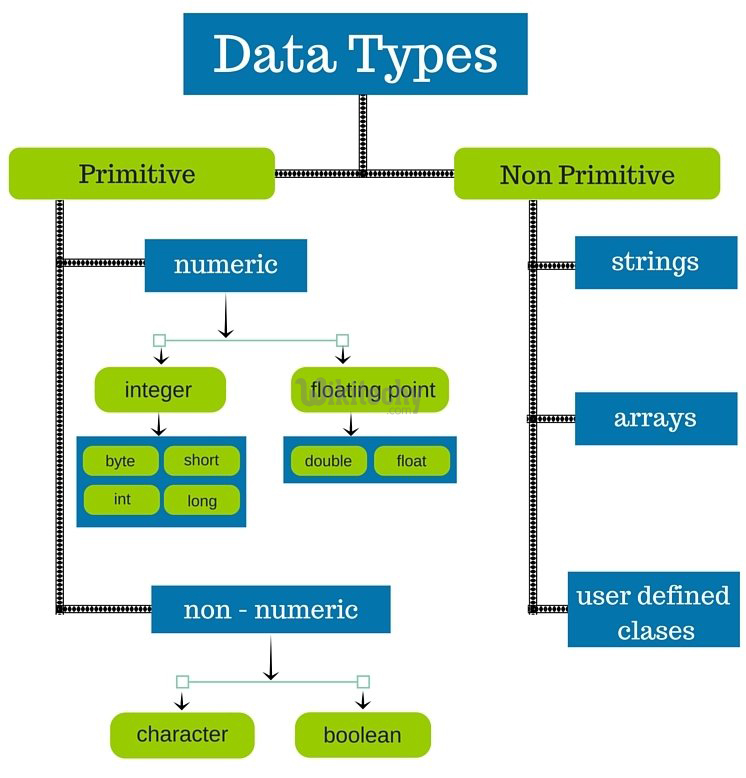
The PHP 7 Data types are Given Below with their definition and examples.
PHP Integers
Integers are whole numbers, without a decimal point (…, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, …). Integers can be specified in decimal (base 10), hexadecimal (base 16 – prefixed with 0x) or octal (base 8 – prefixed with 0) notation, optionally preceded by a sign (- or +).
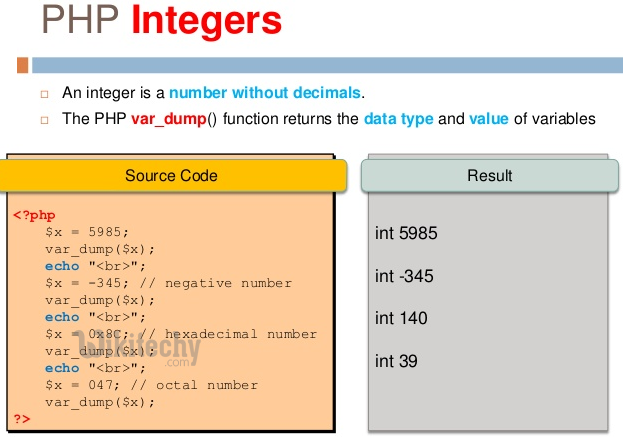
<?php $a = 123; // decimal number var_dump($a); echo "<br>"; $b = -123; // a negative number var_dump($b); echo "<br>"; $c = 0x1A; // hexadecimal number var_dump($c); echo "<br>"; $d = 0123; // octal number var_dump($d); ?>
Note: Since PHP 5.4+ you can also specify integers in binary (base 2) notation. To use binary notation precede the number with 0b (e.g.
$var = 0b11111111;).
PHP Strings

Strings are sequences of characters, where every character is the same as a byte. A string can hold letters, numbers, and special characters and it can be as large as up to 2GB (2147483647 bytes maximum). The simplest way to specify a string is to enclose it in single quotes (e.g. ‘Hello world!’), however, you can also use double quotes (“Hello world!”).
<?php $a = 'Hello world!'; echo $a; echo "<br>"; $b = "Hello world!"; echo $b; echo "<br>"; $c = 'Stay here, I\'ll be back.'; echo $c; ?>
You will learn more about strings in PHP Strings tutorial.
PHP Floating Point Numbers or Doubles
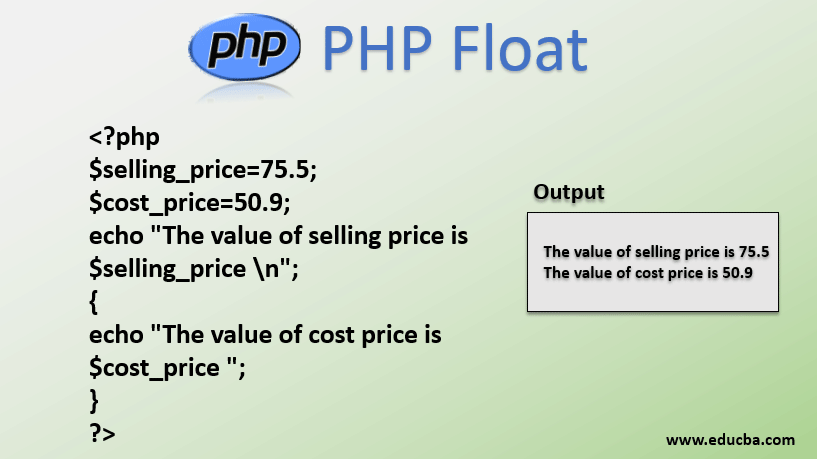
Floating point numbers (also known as “floats”, “doubles”, or “real numbers”) are decimal or fractional numbers as demonstrated in the example below.
<?php $a = 1.234; var_dump($a); echo "<br>"; $b = 10.2e3; var_dump($b); echo "<br>"; $c = 4E-10; var_dump($c); ?>
PHP Booleans
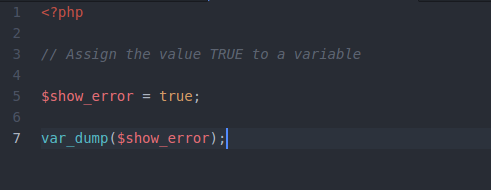
Booleans are like a switch it has only two possible values either 1 (true) or 0 (false).
<?php // Assign the value TRUE to a variable $show_error = True; var_dump($show_error); ?>
PHP Arrays
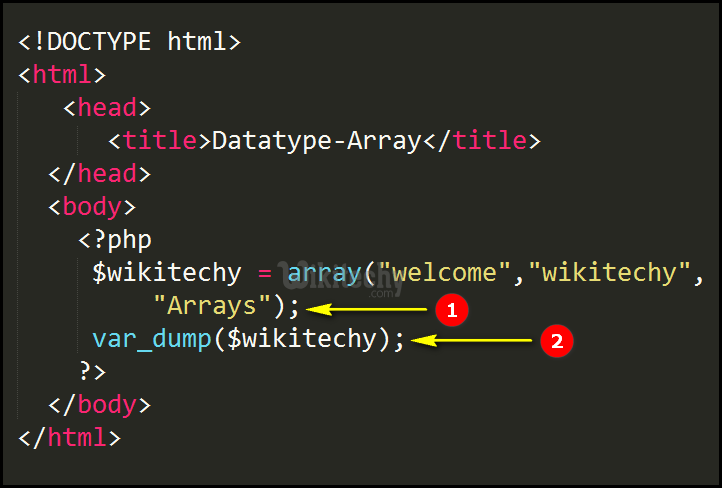
An array is a variable that can hold more than one value at a time. It is useful to aggregate a series of related items together, for example, a set of country or city names. An array is formally defined as an indexed collection of data values. Each index (also known as the key) of an array is unique and references a corresponding value.
<?php
$colors = array("Red", "Green", "Blue");
var_dump($colors);
echo "<br>";
$color_codes = array(
"Red" => "#ff0000",
"Green" => "#00ff00",
"Blue" => "#0000ff"
);
var_dump($color_codes);
?>
You will learn more about arrays in PHP Array tutorial.
PHP Objects
An object is a data type that not only allows storing data but also information on, how to process that data. An object is a specific instance of a class that serves as templates for objects. Objects are created based on this template via the new keyword.
Every object has properties and methods corresponding to those of its parent class. Every object instance is completely independent, with its own properties and methods, and can thus be manipulated independently of other objects of the same class.
Here’s a simple example of a class definition followed by object creation.
<?php
// Class definition
class greeting{
// properties
public $str = "Hello World!";
// methods
function show_greeting(){
return $this->str;
}
}
// Create object from class
$message = new greeting;
var_dump($message);
?>
Tip: The data elements stored within an object are referred to as its properties and the information, or code which describing how to process the data is called the methods of the object.
PHP NULL
The special NULL value is used to represent empty variables in PHP. A variable of type NULL is a variable without any data. NULL is the only possible value of type null.
<?php $a = NULL; var_dump($a); echo "<br>"; $b = "Hello World!"; $b = NULL; var_dump($b); ?>
$var; it is automatically assigned a value of null. Many novice PHP developers mistakenly considered both $var1 = NULL; and $var2 = ""; are the same, but this is not true. Both variables are different — the $var1 has a null value while $var2 indicates no value assigned to it. ![]()
